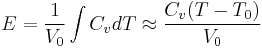Mie–Gruneisen equation of state
The Mie-Gruneisen equation of state is a relation between the pressure and the volume of a solid at a given temperature. It is often used to determine the pressure in a shock-compressed solid. Several variations of the Mie-Gruneisen equation of state are in use.
Contents |
Expressions for the Mie-Gruneisen equation of state
A temperature-corrected version that is used in computational mechanics has the form[1] (see also [2], p.61)
where 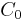 is the bulk speed of sound,
is the bulk speed of sound,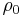 is the initial density,
is the initial density, 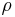 is the current density,
is the current density, 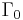 is the Gruneisen's gamma at the reference state,
is the Gruneisen's gamma at the reference state, 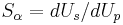 is a linear Hugoniot slope coefficient,
is a linear Hugoniot slope coefficient, 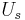 is the shock wave velocity,
is the shock wave velocity, 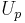 is the particle velocity, and
is the particle velocity, and 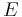 is the internal energy per unit reference specific volume.
is the internal energy per unit reference specific volume.
A rough estimate of the change in internal energy can be computed using
where 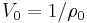 is the reference specific volume at temperature
is the reference specific volume at temperature 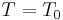 , and
, and 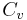 is the specific heat at constant volume. In many simulations, it is assumed that
is the specific heat at constant volume. In many simulations, it is assumed that 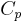 and
and 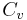 are equal.
are equal.
Parameters for various materials
| material | 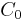 (m/s) (m/s) |
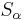 |
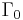 ( (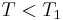 ) ) |
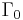 ( (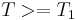 ) ) |
T_1 (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 3933 [3] | 1.5 [3] | 1.99 [4] | 2.12 [4] | 700 |
See also
References
- ^ Zocher, M.A.; Maudlin, P.J. (2000), "An evaluation of several hardening models using Taylor cylinder impact data", Conference: COMPUTATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING, BARCELONA (ES), 09/11/2000--09/14/2000, http://www.osti.gov/energycitations/product.biblio.jsp?osti_id=764004, retrieved 2009-05-12
- ^ Wilkins, M.L. (1999), Computer simulation of dynamic phenomena, http://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en, retrieved 2009-05-12
- ^ a b Mitchell, A.C.; Nellis, W.J. (1981), "Shock compression of aluminum, copper, and tantalum", Journal of Applied Physics 52: 3363, http://link.aip.org/link/?JAPIAU/52/3363/1, retrieved 2009-05-12
- ^ a b MacDonald, R.A.; MacDonald, W.M. (1981), "Thermodynamic properties of fcc metals at high temperatures", Physical Review B 24 (4): 1715–1724, doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.24.1715
![p = \frac{\rho_0 C_0^2 (\eta -1)
\left[\eta - \frac{\Gamma_0}{2}(\eta-1)\right]}
{\left[\eta - S_{\alpha}(\eta-1)\right]^2} %2B \Gamma_0 E;\quad
\eta�:= \cfrac{\rho}{\rho_0}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/044b6ce7616c73939e6983daba3921ec.png)